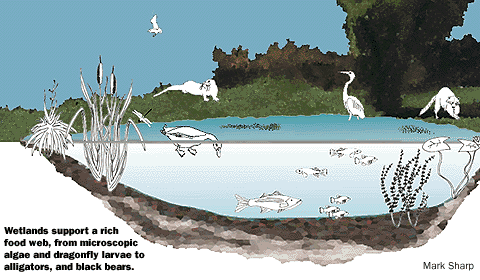
 Wetlands - Food Web Relationships
Wetlands - Food Web Relationships
"When we try to pick out anything by itself, we find it hitched to everything else in the Universe" -- John Muir
![]() 1. Read - Food Chains and Webs | Watch - Food Chain on YouTube (Stop the video to take notes when you need to.)
1. Read - Food Chains and Webs | Watch - Food Chain on YouTube (Stop the video to take notes when you need to.)
Helpful resources: Ecology | Ecology and food webs in wetlands | Fabulous Food Chains - video
Pond Ecosystem: Types, Food Chain, Animals and plants
Wetlands food chains video
Ecosystems - producers, consumers and decomposers video (Which one are you?)
Hey Now Science - Producers, comsumers and decomposers (Which level of consumer are you? Primary, secondary or tertiary)
![]() 2. Create a matrix (Need help? - Matrices @ Math Dude. Hey, he is fun!)
2. Create a matrix (Need help? - Matrices @ Math Dude. Hey, he is fun!) ![]()
Use the first Row to label the columns - Species - Predator - Prey - Producer - Consumer - Decomposer -
Parasite - Host, Autotrophs - Heterotrophs.Down the first column enter one species in each row. (Examine at least 8 organisms from 5 different Classes.)
![]() 3. Use the matrix to sort out the relationships.
3. Use the matrix to sort out the relationships.
For each species:
Ask yourself - Is it a predator? If yes, place a
checkmark in the cell.
If no, leave the cell blank.Continue through each column for the species. Do all the species rows.
![]() 4. Examine the matrix - What have you found?
4. Examine the matrix - What have you found?
How many of the animals are predators?
What percentage of the animals are prey?
How many of the organism are producers? What percentage are consumers?
How many are Autotrophs? What percentage are Heterotrophs?
Which relationship is the most essential to the ecosystem?
Which species is the least important to the ecological balance of a wetland?
Identify 4 food chains using wetland species.
What conclusion(s) can you come to based on these observations?
Extend your efforts:
![]() Draw a food web of wetlands organisms. Show the flow of energy.
Draw a food web of wetlands organisms. Show the flow of energy.
(You do not have to draw pictures. Use public domain images. If you prefer, type the names and draw the arrows using the draw arrow tool.)
![]() Make a food web vocabulary crossword puzzle. (Doing this will help you learn all this new vocabulary.)
Make a food web vocabulary crossword puzzle. (Doing this will help you learn all this new vocabulary.)
![]() Wetlands: Habitat / Mammals / Birds / Aquatic insects / Plants & trees / Amphibians / Lentic or Lotic ecosystem?
Wetlands: Habitat / Mammals / Birds / Aquatic insects / Plants & trees / Amphibians / Lentic or Lotic ecosystem?
Wetland Poem Project / Froggy Fact song / Wetland Photos / Wetland Vocabulary Exercise
Wetland food web / Eagles Evaluate / Frog & Amphibian Facts Activity / Wetland Ecology Dilemmas
School Habitat Garden Project / Birds: Nest and Rearing / Water & Watershed Studies
Bats are our Buddies / Bats at the Beach Activity / Ecology Vocabulary Exercise
Water Wars | Pennsylvania HS Envirothon | Plants and People | Groundwater Studies | Monitor Wetland
Posted 7/2008 by Cindy O'Hora, Updated 4/2024
![]() Save a tree - How to make a Digital Answer Sheet: Highlight the text of the questions on this web page, copy them - Edit .. Copy. Open a text document or word processing document. Paste the questions into the blank document. Answer the questions in the word processing document in a contrasting color (NOT YELLOW) or font (avoid fancy fonts like:
Save a tree - How to make a Digital Answer Sheet: Highlight the text of the questions on this web page, copy them - Edit .. Copy. Open a text document or word processing document. Paste the questions into the blank document. Answer the questions in the word processing document in a contrasting color (NOT YELLOW) or font (avoid fancy fonts like: ![]() , Symbol,
, Symbol, ![]() or
or ![]() ). Save frequently as you work. I do not like losing my work. You will not like it either. Submit your assignment via an electronic class dropbox or email attachment. Save a copy of your work on your computer.
). Save frequently as you work. I do not like losing my work. You will not like it either. Submit your assignment via an electronic class dropbox or email attachment. Save a copy of your work on your computer.
Proof read your responses. It is funny how speling errors and typeos sneak in to the bets work. ![]()
Make Your Own Printed answer sheet. Tech Tip: Working in a group or in two different places like the library & home? You do not have to be physically together to work together. ![]() Watch Google Docs video TAI - How could you use free, Google Docs to do a project? How would this facilitate group projects?
Watch Google Docs video TAI - How could you use free, Google Docs to do a project? How would this facilitate group projects?
Pennsylvania Science Anchors Science NetLinks Benchmark 5 - The Living Environment D. Interdependence of Life - " In all environments freshwater, marine, forest, desert, grassland, mountain, and others organisms with similar needs may compete with one another for resources, including food, space, water, air, and shelter. Two types of organisms may interact with one another in several ways: They may be in a producer/consumer, predator/prey, or parasite/host relationship." |